Contents
- 1 Cat Body Language
- 1.1 How to Interpret Cat Body Language
- 1.2 Decoding Cat Ear Positions and Meanings
- 1.3 What Cat Vocalizations Tell You About Their Mood
- 1.4 Contextualizing Vocalizations
- 1.5 Analyzing Your Cat’s Posture for Better Communication
- 1.6 Recognizing and Understanding Cat Movement Patterns
- 1.7 Play Behavior and Its Significance
- 1.8 Conclusion
Cat Body Language
Cat Body Language: Tail, Ear, Eye & More Understanding your cat’s body language is essential for building a strong and harmonious relationship. Cats communicate primarily through their body, and by learning to interpret their signals, you can better meet their needs and ensure their well-being. This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of cat body language, focusing on tail, ear, eye, vocalizations, posture, and movement. Whether you’re a new cat owner or looking to deepen your understanding, this article will equip you with the knowledge to decode your feline friend’s non-verbal cues.
How to Interpret Cat Body Language
Understanding Tail Positions
A cat’s tail is a powerful indicator of their emotions and intentions. Different positions can signify a range of feelings from contentment to agitation.
Upright Tail: A cat holding its tail straight up typically signifies confidence and friendliness. This is often seen when a cat approaches you or another cat in a friendly manner.

Puffed-Up Tail: A tail that is puffed up indicates that the cat is frightened or startled. This is a defensive posture intended to make the cat appear larger to potential threats.

Tail Twitching: Rapid twitching or flicking of the tail may signal irritation or annoyance. If the tail is twitching while the cat is focused on something, it might indicate excitement or concentration.

Low or Tucked Tail: A tail tucked close to the body usually signifies fear or submission. The cat may feel threatened and is trying to make itself less noticeable.
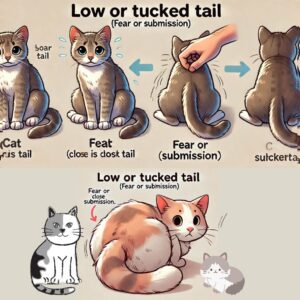
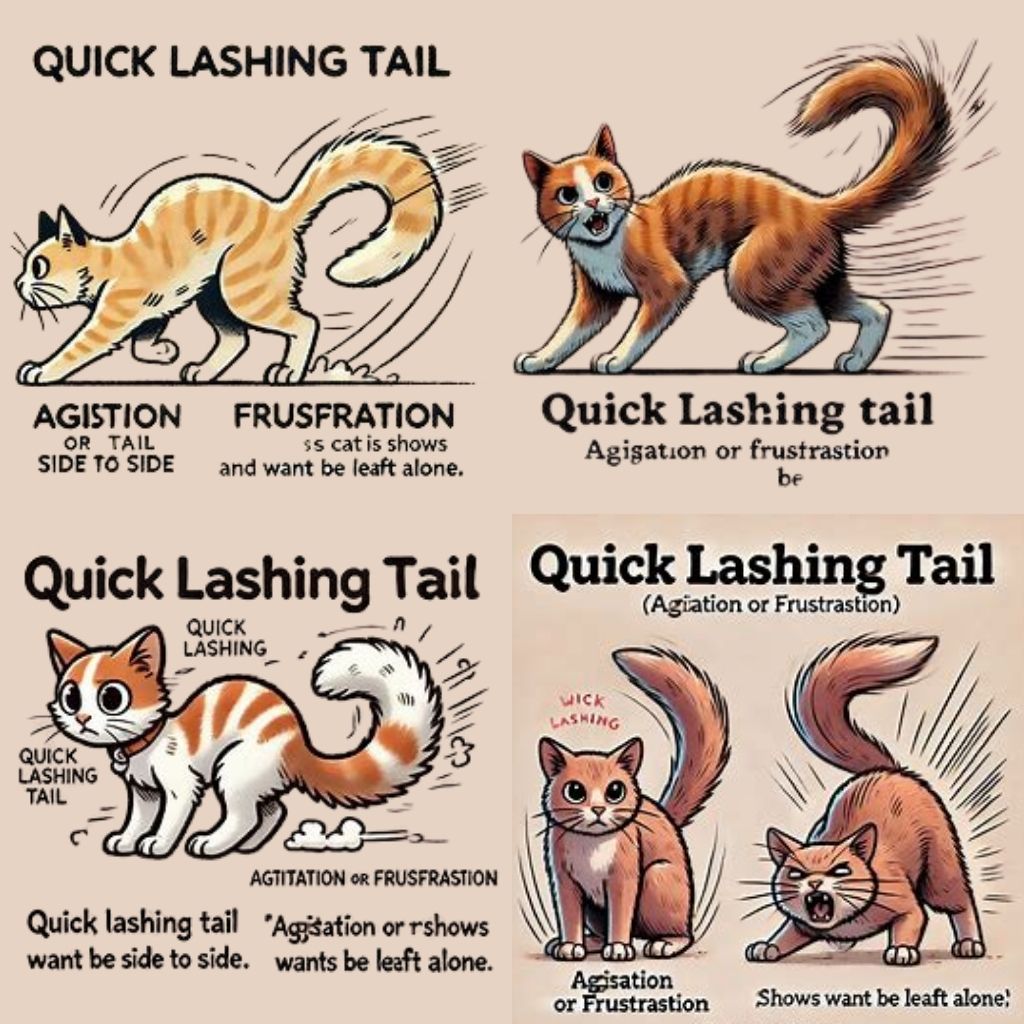
Tail Movements and Their Meanings
Beyond static positions, the way a cat moves its tail can convey additional information.
- Slowly Swishing Tail: Gentle swishing can indicate that a cat is relaxed but alert. It may be contemplating whether to engage or retreat.
- Quick Lashing: Fast lashing of the tail typically denotes agitation or frustration. It’s a clear sign that the cat wants to be left alone.
- Wrapped Tail: When a cat wraps its tail around another cat or a person, it is a sign of affection and bonding.
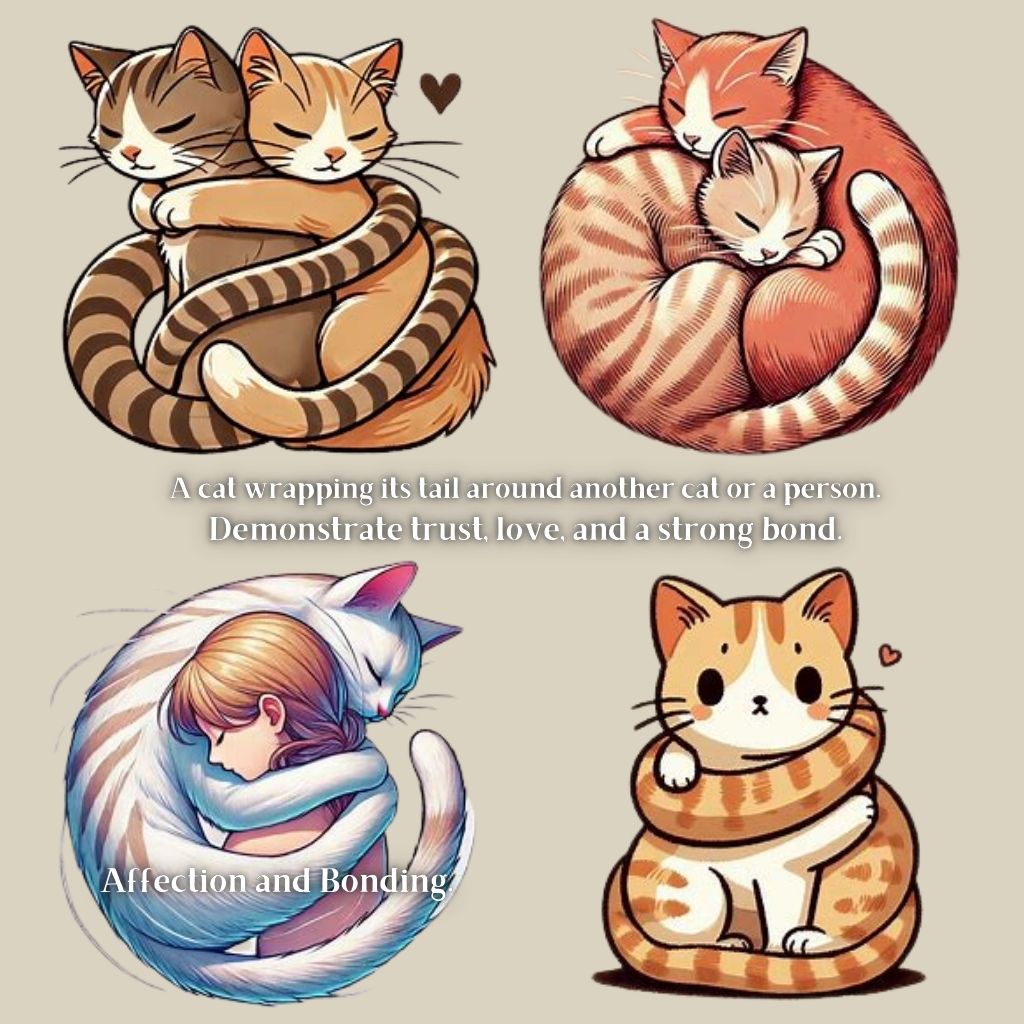


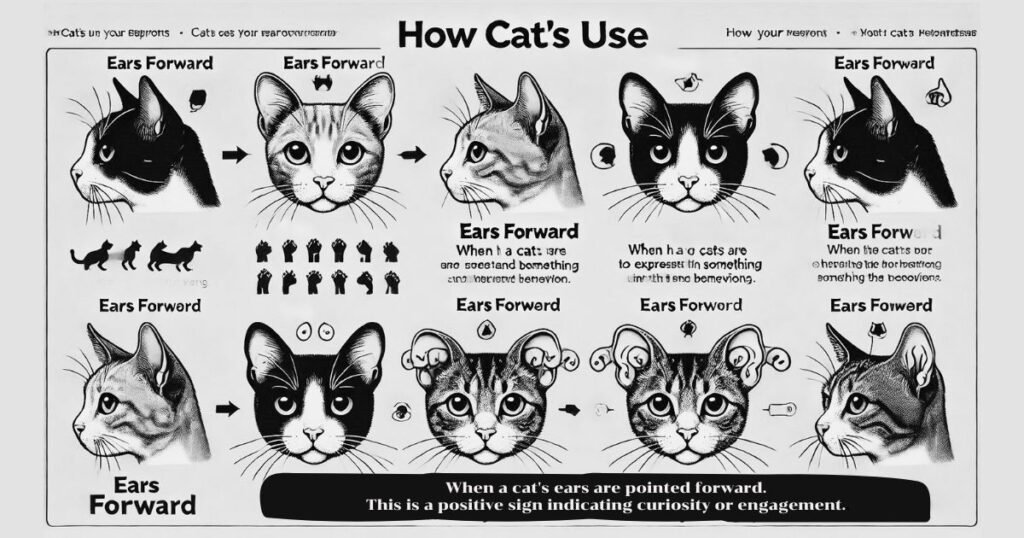
Decoding Cat Ear Positions and Meanings
Ear Positions and Their Signals
A cat’s ears are highly expressive and can provide significant insight into their current state of mind.
- Ears Forward: When a cat’s ears are pointed forward, it usually means they are alert and interested in something in their environment. This is a positive sign indicating curiosity or engagement.
- Ears Flattened Back: Ears flattened against the head signal that the cat is frightened, angry, or feeling threatened. This defensive posture is a warning to stay away.
- Ears Sideways: If a cat’s ears are swaying from side to side, it may indicate that they are uncertain or confused about something.
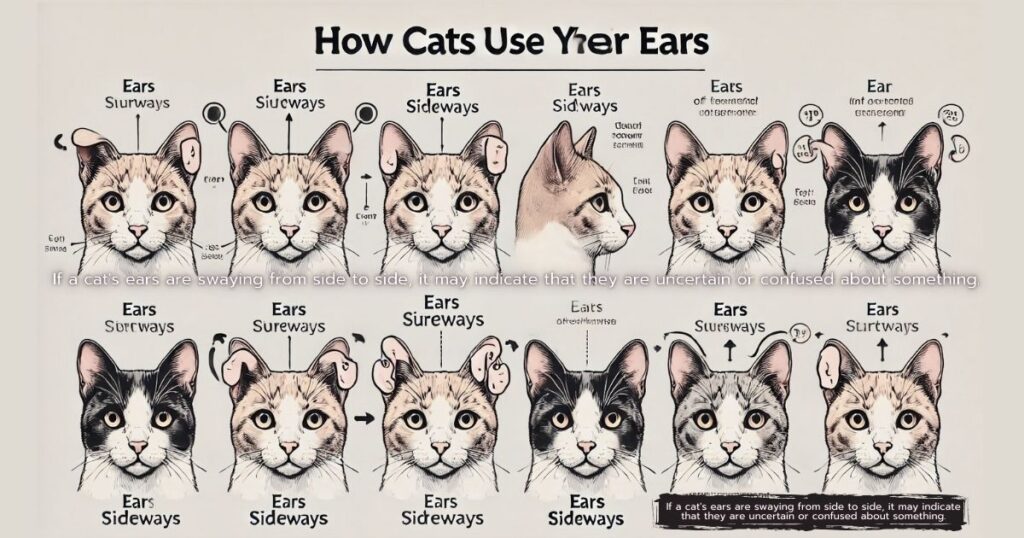


Subtle Ear Movements
Minor adjustments in ear positioning can also convey nuanced emotions.
- Rapidly Moving Ears: Quick movements can show that the cat is agitated or irritated.
- Relaxed Ears: Slightly relaxed ears indicate that the cat is calm and comfortable in their environment.


Understanding Cat Eye Signals and What They Reveal
Eye Shapes and Their Meanings
A cat’s eyes can reveal a lot about their emotions and intentions through their shape and behavior.
- Wide Open Eyes: When a cat’s eyes are wide open, it signifies alertness and attentiveness. The cat is fully engaged with their surroundings.
- Narrowed Eyes: Narrowed or squinted eyes can indicate that the cat is relaxed and content. It can also be a sign of affection when the cat is gazing at you softly.


Slow Blinking: Slow blinking is a sign of trust and affection. If your cat slowly blinks at you, it’s a way of saying they feel safe and comfortable.
Pupil Size and What It Indicates
The size of a cat’s pupils can also provide clues about their emotional state.
- Dilated Pupils: Dilated pupils can indicate excitement, fear, or aggression. It often occurs when the cat is startled or aroused.
- Constricted Pupils: Smaller pupils are a sign of contentment and relaxation. When a cat is at ease, their pupils may be naturally smaller.


What Cat Vocalizations Tell You About Their Mood
Common Vocalizations and Their Meanings
Cats use a variety of sounds to communicate their needs and feelings.
- Meowing: Cats meow to communicate with humans. The tone and pitch can vary depending on what the cat wants, such as attention, food, or to be let outside.
- Purring: Purring generally indicates that a cat is content and comfortable. However, cats may also purr when they are in pain or feeling anxious as a self-soothing mechanism.
- Hissing: A hiss is a clear sign that a cat is feeling threatened, scared, or angry. It’s a defensive vocalization meant to ward off potential threats.
- Chirping and Chattering: These sounds often occur when a cat is watching birds or other prey. It can indicate excitement and frustration at not being able to reach the target.
Contextualizing Vocalizations
Understanding the context in which the vocalizations occur is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Time of Day: Some cats are more vocal at certain times, such as dawn or dusk, which are their natural hunting times.
Environmental Factors: Changes in the environment, such as moving to a new home or the introduction of a new pet, can influence how much a cat vocalizes.
Environmental Factors: Changes in the environment, such as moving to a new home or the introduction of a new pet, can influence how much a cat vocalizes.
Analyzing Your Cat’s Posture for Better Communication
Common Postures and Their Interpretations
A cat’s overall posture can provide comprehensive insights into their emotional and physical state.
- Arched Back: An arched back often signifies that the cat is scared or trying to appear larger to deter threats.
- Crouched Posture: When a cat is crouched low to the ground, it indicates fear or readiness to pounce. This posture can be a sign of both aggression and playfulness.
- Relaxed Posture: A relaxed and loose body posture indicates that the cat feels safe and comfortable. The cat may be lounging or sleeping in this state.
- Standing Tall: Standing tall with an erect posture shows confidence and dominance. This posture is often seen when a cat is exploring or surveying its territory.

Combining Posture with Other Signals
To accurately interpret posture, consider it alongside other body language cues such as tail and ear positions.
- Confident and Content: A cat standing tall with ears forward and tail upright is likely feeling confident and content.
- Fearful and Anxious: A crouched posture with flattened ears and a tucked tail indicates that the cat is fearful or anxious.
Recognizing and Understanding Cat Movement Patterns
Types of Movements and Their Meanings
A cat’s movements, whether subtle or swift, can convey a range of emotions and intentions.
- Slow Movements: Slow and deliberate movements often indicate that the cat is cautious or curious. It may be exploring a new environment or approaching something unfamiliar.
- Quick, Sudden Movements: Rapid movements can signal excitement, playfulness, or aggression. Quick dashes across the room may be part of a playful chase or a sudden burst of energy.
- Stretching and Yawning: Stretching is a sign of relaxation and contentment. Yawning can indicate that the cat is feeling sleepy or may be experiencing mild stress.
Play Behavior and Its Significance
Understanding play behavior is essential for recognizing when a cat is in a playful mood versus when they may be overstimulated.
- Chasing and Pouncing: These movements are typical during play and simulate hunting behaviors. It’s a positive sign that the cat is active and engaged.
- Biting and Scratching: Gentle biting and scratching during play indicate that the cat is enjoying interaction, but it’s important to set boundaries to prevent aggressive behavior.
Integrating All Body Language Cues
To fully understand your cat’s emotions and needs, it’s important to consider all aspects of their body language collectively.
- Consistent Signals: When multiple signals align, such as an upright tail, forward ears, and relaxed posture, it clearly indicates that the cat is happy and content.
- Conflicting Signals: If signals contradict each other, such as a relaxed posture with a twitching tail, it may indicate mixed emotions or that the cat is processing something internally.



Building a Stronger Relationship Through Understanding
By mastering your cat’s body language, you can respond appropriately to their needs, enhancing the bond you share.
- Responding to Stress: Recognizing signs of stress allows you to create a more comfortable environment for your cat, reducing anxiety and promoting well-being.
- Encouraging Positive Behavior: Understanding what makes your cat feel happy and secure helps you encourage behaviors that strengthen your relationship.
Conclusion
Decoding Cat Body Language is a valuable skill that enhances communication and deepens your relationship with your feline companion. By paying attention to tail positions, ear movements, eye signals, vocalizations, posture, and overall movement patterns, you can gain profound insights into your cat’s emotional state and needs. This understanding not only ensures your cat’s well-being but also fosters a harmonious and loving environment for both of you. Remember, every cat is unique, and with patience and observation, you can become adept at interpreting their subtle and not-so-subtle cues.




